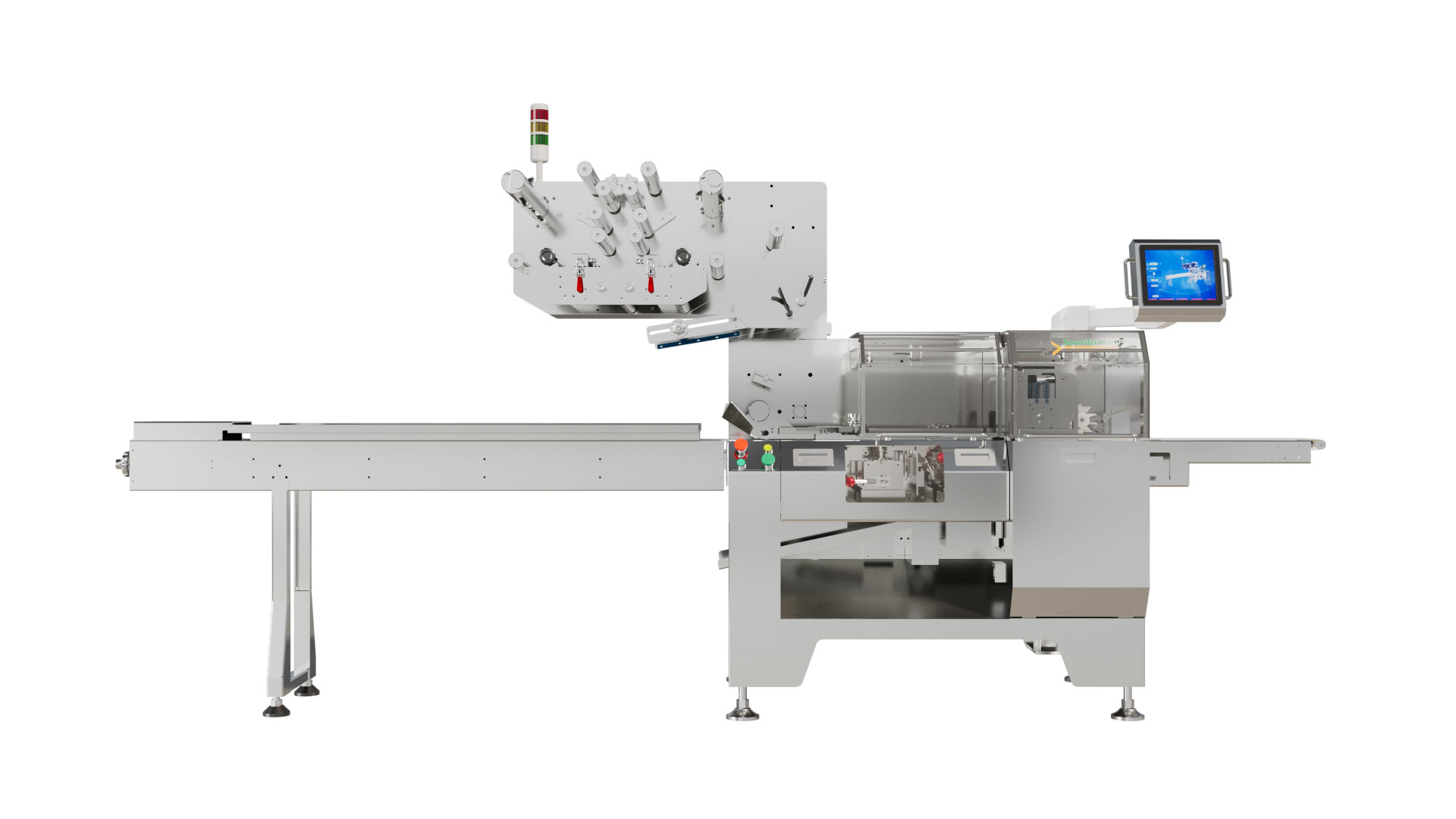
Packaging Machine Encyclopedia: Core Guides & Solutions for Modern Packaging
Packaging Knowledge Hub

If you're seeking packaging automation solutions, please contact us, and we'll be delighted to offer you the most tailored solution.
Modern packaging machinery is no longer just about sealing products into a bag or box. Today's manufacturers need flexible, automated systems that support multiple SKUs, meet food safety standards, reduce labor pressure, and connect smoothly with upstream processing and downstream logistics.
This Packaging Machine Encyclopedia brings together Soontrue's core knowledge on packaging machines and packaging automation. From basic definitions and machine types to food packaging solutions and fully automated packaging lines, this hub page helps you quickly find the right guide for your role and your project.
Whether you search for packaging machine, packing machine, or automated packaging line, this is the best place to start.
1. What Is the Packaging Machine Encyclopedia?
The Packaging Machine Encyclopedia is Soontrue's structured knowledge base for packaging equipment and packaging lines. It is designed for:
- Factory owners and plant managers – who need a high-level understanding of options and investment decisions.
- Engineers and technical teams – who care about machine types, components, formats, and integration.
- Distributors and integrators – who want to explain solutions clearly to their own customers.
- Newcomers to the packaging industry – who need a simple, reliable place to learn the basics.
Instead of reading scattered articles, you can follow a clear path:
- Start with basic concepts – what a packaging machine is and how different types work.
- Move on to bag types and pack formats – how your marketing and channels affect packaging design.
- Explore food packaging solutions and automated packaging lines – full-line thinking from product to pallet.
- Finally, dive into industry-specific solutions and product pages that match your actual project.
All the guides listed on this hub are part of the Soontrue Packaging Knowledge Series, and each one is connected to real-world projects in bakery, biscuits, snacks, noodles, frozen food, coffee powder, pet food, and more.
2. Core Guides (Main Articles 1–6)
This section links to the six core guides in the Packaging Machine Encyclopedia. Each guide covers a different part of the knowledge system.
2.1 Packaging Machine Definition & History
This guide explains how packaging evolved from manual packing to semi-automatic machines, then to fully automatic packaging machines and finally intelligent, vision-assisted packaging systems.
You will learn:
- What a packaging machine is in modern manufacturing.
- Key milestones in the history of packaging automation.
- How trends such as high-speed lines, smart factories, and sustainable packaging are shaping equipment design.
2.2 Types of Packaging Machines & Working Principles
This guide gives you a structured overview of the main packaging machine types and how they work, including:
- Horizontal Flow Wrapping Machines (Flow Wrappers / Pillow Packing Machines) – continuous wrapping for biscuits, bakery products, noodles, and snack bars.
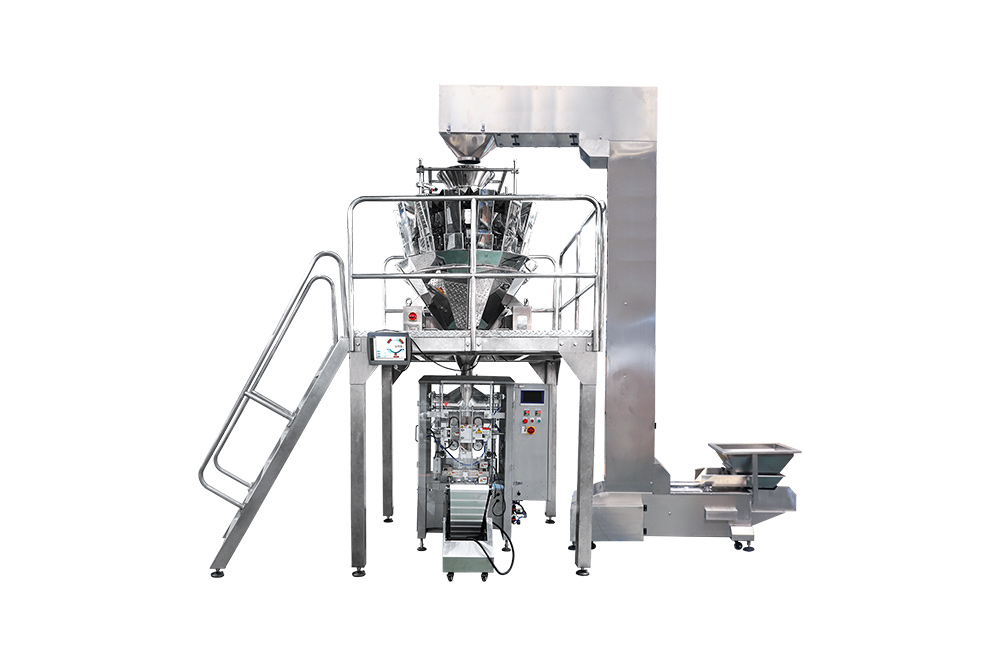
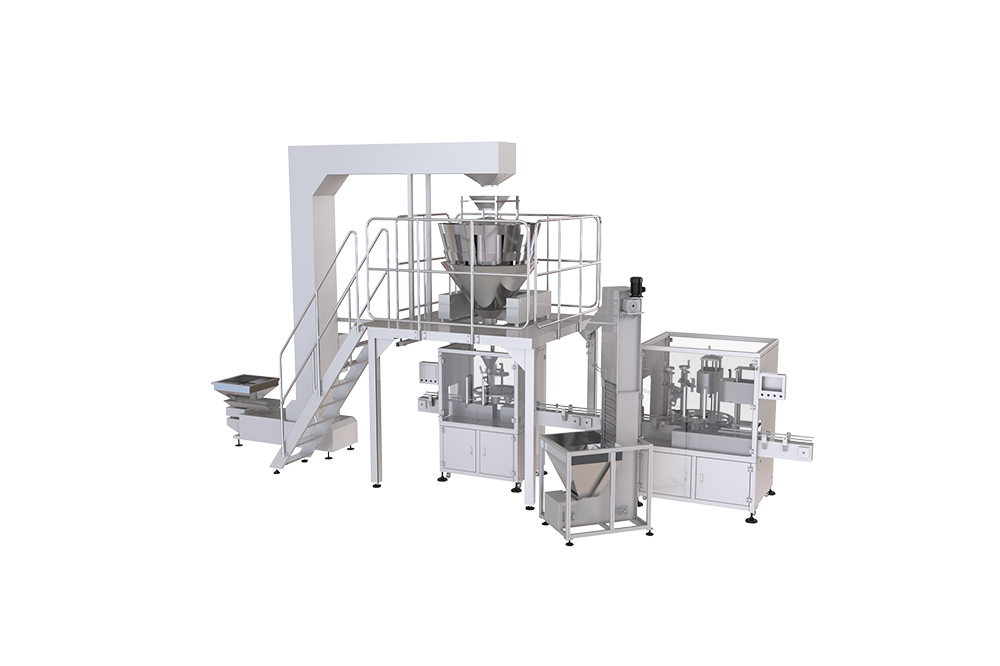
- Vertical Form-Fill-Seal Machines (VFFS Packaging Machines) – forming, filling, and sealing bags for granules, powders, and frozen foods from a film roll.
- Premade Pouch Packing Machines – filling and sealing prefabricated pouches such as stand-up pouches and zipper pouches.
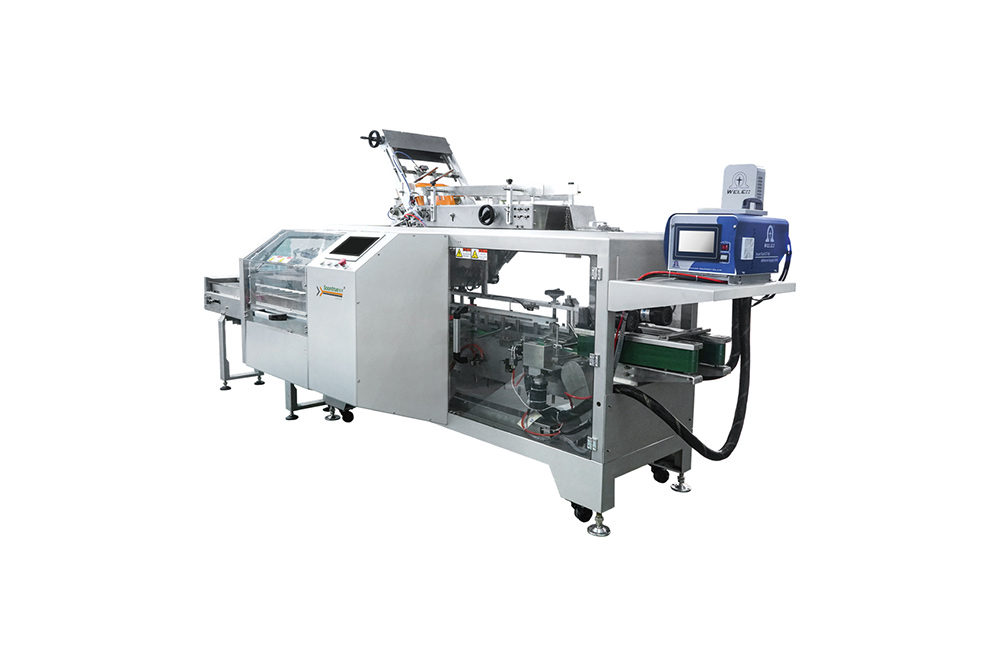
- Cartoning Machines (Cartoners) – loading bags, trays, or products into cartons for retail.
- Case Erecting Machines (Case Erectors) – forming and sealing corrugated cases from flat blanks.
- Case Packing Machines – top-load, side-load, or wrap-around packing of products or cartons into cases.
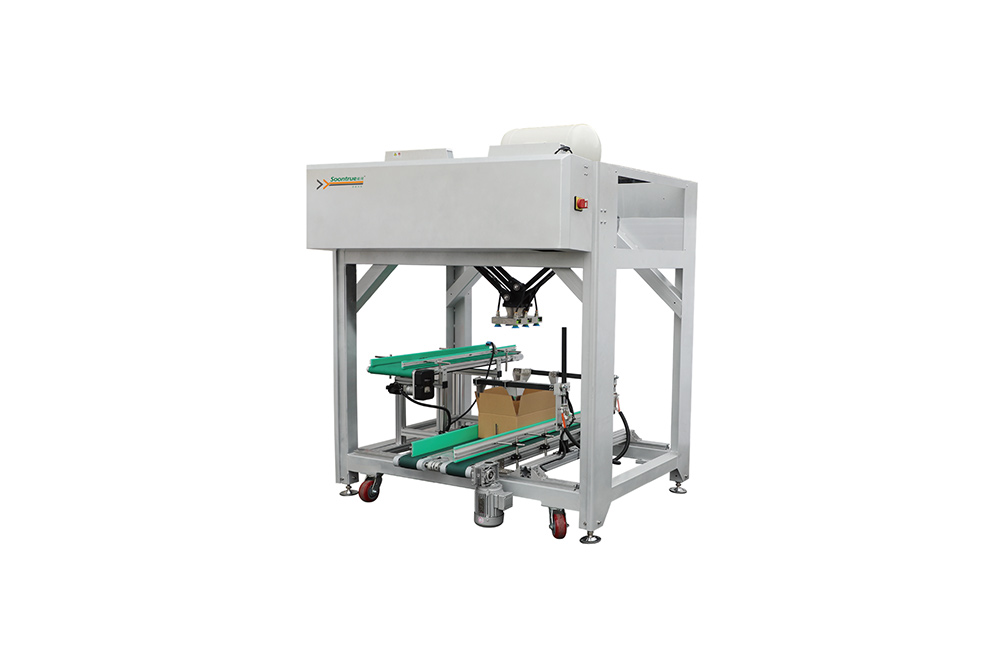
- Palletizing Systems – robotic palletizers and palletizing lines for end-of-line automation.
You will also see typical working principles, motion types (rotary vs. box motion), and basic pros and cons of each machine type.
2.3 Key Components of Packaging Machines
This guide focuses on the core components that make modern packaging machinery stable, flexible, and efficient:
- Feeding and infeed systems – conveyors, pushers, distribution systems, and automatic feeding for bakery and snack lines.
- Forming and sealing units – forming tubes, sealing jaws, box-motion or rotary sealing, temperature control, and film tracking.
- Dosing and filling systems – multihead weighers, auger fillers, volumetric cup fillers, liquid pumps, and combination systems.
- Control systems & drives – PLCs, HMIs, servo motors, motion control, sensors, and vision systems.
- Safety & hygiene design – guarding, stainless steel structures, clean design for food contact areas.
Understanding components helps you evaluate different suppliers and decide what you really need in your factory.
2.4 Common Bag Types & Pack Formats
This guide explains the bag types and pack formats most frequently used in food and non-food packaging, such as:
- Pillow bags / pillow packs
- Gusseted bags and block-bottom bags
- Stand-up pouches (with or without zipper or spout)
- Stick packs and 3-side-seal sachets
- Chain bags / linked packs for multi-packs
- Trays with film overwrap
- Cartons and display boxes for retail shelves
- Cases and transport cartons for export and logistics
You will learn how pack formats relate to:
Product type (solid, powder, liquid, frozen)
Sales channel (retail, wholesale, food service, e-commerce)
Brand positioning and shelf impact
Film/material choice and sealing performance
2.5 What Is a Food Packaging Solution?
This guide is a full-line view of food packaging solutions. It explains what a complete food packaging line looks like from product feeding to pallet:
- How to combine flow wrapping machines, VFFS packaging machines, and premade pouch packing machines with weighing and filling systems.
- How to handle applications such as bread and bakery, biscuits and cookies, snacks and puffed foods, noodles, dried fruits and nuts, coffee powder, frozen foods, and pet food.
- How to connect primary packaging to cartoning, case erecting, case packing, case sealing, and palletizing.
It also provides a step-by-step method for choosing the right food packaging system based on your product, format, speed, hygiene requirements, and factory layout.
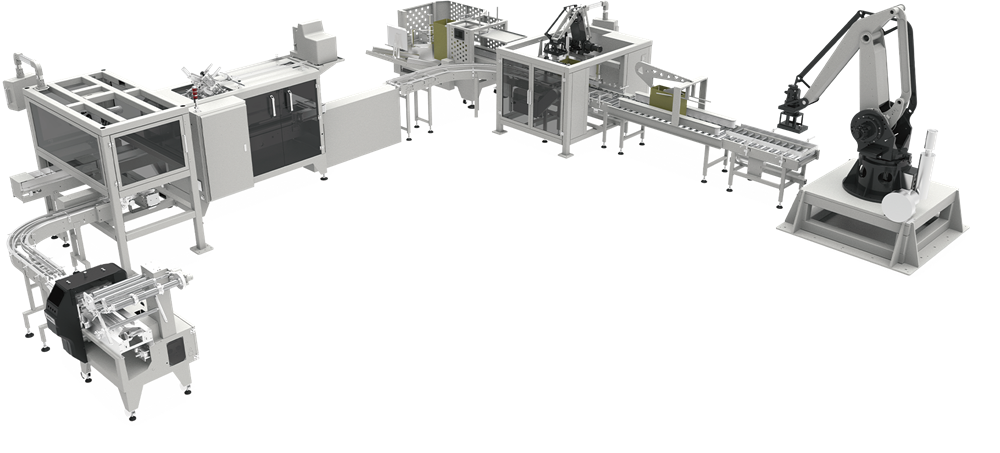
2.6 What Is an Automated Packaging Line / End-of-Line Solution?
This guide explains how to connect multiple packaging machines into a fully automated packaging line, with a special focus on end-of-line packaging:
- The role of automatic feeding and distribution systems between processing and primary packaging.
- How cartoners, case erectors, case packers, and palletizers work together.
- Typical layouts for bakery, snack, frozen food, and mixed-SKU production.
- How to plan an end-of-line project: scope, capacity, layout, and integration with existing equipment.
If you are planning smart factory upgrades or looking to reduce manual packing, this guide shows the big picture.
3. Industry and Application Solutions
Beyond the six core guides, the Packaging Machine Encyclopedia connects to a series of industry and application-specific packaging solutions. These solution pages apply the core concepts to real materials and products, including food, powders, liquids, non-food goods, and pharmaceutical / healthcare items.
You can explore solutions from several different angles: by industry, by material type, or by machine family.
3.1 Food Industry Packaging Solutions
Soontrue provides food packaging solutions for a wide range of product categories. Typical applications include:
• Bread & Bakery Packaging Solutions – sliced bread, toast, buns, cakes, Swiss rolls.
• Biscuit & Cookie Packaging Solutions – sandwich biscuits, cookies, crackers, wafers.
• Chocolate & Confectionery Packaging Solutions – chocolate bars, tablets, pralines, coated products, candies.
• Snack & Puffed Food Packaging Solutions – chips, popcorn, puffed snacks, extruded snacks.
• Noodle Packing Solutions – instant noodles, noodle blocks with sachets, dry noodles.
• Dried Fruits & Nuts Packaging Solutions – raisins, dates, mixed dried fruits, nuts, seeds.
• Coffee Powder & Ground Coffee Packaging Solutions – bags, sachets, stand-up pouches.
• Frozen Food Packaging Solutions – dumplings, buns, vegetables, seafood, meat.
• Pet Food & Animal Feed Packaging Solutions – small pouches to 10–50 kg bags.
3.2 Powder and Granule Packaging Solutions
Powder and granule products can be either food or non-food. They usually rely on vertical form-fill-seal (VFFS) packaging machines, premade pouch packing machines, and appropriate dosing systems, such as multihead weighers, auger fillers, and volumetric cup fillers.
Typical powder and granule packaging solutions include:
• Food powders – flour, milk powder, coffee powder, cocoa, drink mixes, spice blends.
• Food granules – sugar, salt, rice, beans, cereal, snack pellets.
• Household and industrial powders – washing powder, detergents, cleaning powders.
• Agricultural granules – seeds, fertilizers, feed additives (within local regulations).
3.3 Liquid and Semi-Liquid Packaging Solutions
Liquids and semi-liquids require different filling technologies and seal integrity control. Depending on the viscosity and pack format, Soontrue systems can be configured with liquid pumps, piston fillers, or other suitable dosing equipment.
Typical liquid and semi-liquid packaging solutions can include:
• Food liquids – sauces, dressings, edible oils, marinades, condiments.
• Semi-liquid foods – jams, pastes, creams, fillings for bakery or snack applications.
• Household liquids – detergents, cleaning agents, liquid soaps (where applicable).
Most of these applications use sachets, pillow bags, or premade pouches (with or without spout), combined with liquid dosing systems and appropriate sealing profiles.
3.4 Non-Food and Household Packaging Solutions
Non-food products often have very different shapes, weights, and handling requirements, but can still benefit from flow packing, vertical packing, premade pouches, and end-of-line automation.
Typical non-food packaging solutions include:
• Hardware and stationery – screws, fasteners, small tools, pens, erasers, office kits.
• Household goods – sponges, wipes, cloths, small accessories and refills.
• Personal care items – cotton pads, disposable hygiene products (subject to local requirements).
• Industrial components – small parts, fittings, connectors, and kits.
These solutions often focus on counting, grouping, and multi-pack configurations, combined with cartoning and case packing for retail and e-commerce.
3.5 Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Packaging Solutions
For pharmaceutical and healthcare products, packaging usually emphasizes accuracy, traceability, and compliance with local GMP and regulatory requirements. Soontrue’s role is typically in secondary packaging and multi-pack configurations, for example:
• Sachets and small bags for OTC powders and granules (where regulations allow).
• Secondary packaging – cartoning and case packing for blister packs, bottles, or medical devices supplied by upstream equipment.
• Kitting and multi-pack solutions – combining different components into one retail or hospital pack.
Any project in this field must be evaluated case by case to match local regulations, product characteristics, and validation requirements.
3.6 Solutions by Machine Type and Bag Format
In addition to industry- and material-based views, you can also explore solutions by machine type and by bag format:
• Flow Packing Machine Solutions – pillow bags, chain bags, tray plus film packaging.
• Vertical Packaging Machine Solutions – bags from film roll for powders, granules, and frozen products.
• Premade Pouch Packing Machine Solutions – stand-up pouches, zipper pouches, spouted pouches.
• Wrapping Machine and Cartoning Machine Solutions – overwrapping, cartoning, and display-ready packs.
• Case Erecting Machine and Case Packing Machine Solutions – transport cases and logistics-ready packaging.
• End-of-Line and Palletizing Solutions – robotic palletizers and complete end-of-line systems.
4. How to Use This Encyclopedia for Your Project
Different readers can use this Packaging Machine Encyclopedia in different ways.
4.1 If You Are New to Packaging Machinery
- Start with Packaging Machine Definition & History to understand the big picture.
- Read Types of Packaging Machines & Working Principles to see the main machine families.
- Check Common Bag Types & Pack Formats so you know what your products can look like on the shelf.
After that, you will have enough background to talk more confidently with suppliers and internal teams.
4.2 If You Are a Factory Owner or Project Leader
- Read Types of Packaging Machines & Working Principles to understand your options.
- Go to What Is a Food Packaging Solution? and What Is an Automated Packaging Line / End-of-Line Solution? to see how machines become a complete line.
- Find your industry in the Food Packaging Solutions section and open the relevant solution page (bakery, biscuits, frozen food, coffee, etc.).
- Then move to specific machine product pages for detailed specs, speeds, and layout options.
Use this path when you are planning new investments, new plants, or capacity upgrades.
4.3 If You Are a Distributor or Integrator
- Use the core guides (Sections 2.1–2.4) as training material for your sales and technical teams.
- Use the Food Packaging Solutions and machine-type solutions as reference when you discuss projects with your customers.
- Link or share this Encyclopedia hub with customers who need to understand the basics quickly.
This helps you position yourself not just as a reseller, but as a solution partner.
4.4 Turning Knowledge into a Real Project
Reading guides is the first step. The next step is to map this knowledge to your own factory. To move from theory to practice:
- Prepare a simple list of your products, target pack formats, and daily or hourly output.
- Note your current equipment, available floor space, and future expansion plans.
- Use this Encyclopedia to identify which machine types and solutions are most relevant.
- Share this information with Soontrue so we can help you design a practical, scalable packaging solution.
5. About Soontrue
Founded in 1993 in Foshan, China, Soontrue focuses on packaging equipment automation and smart factory solutions. With multiple production bases and a full portfolio of:
- Wrapping and cartoning machines
Soontrue provides integrated packaging systems for customers in bakery, biscuits, snacks, frozen foods, coffee, pet food, and many other industries.
This Packaging Machine Encyclopedia reflects the know-how from years of real projects. It is updated and expanded as new technologies and applications appear in the market.
6. Next Step
If you are planning a new line or upgrading existing equipment, use this Encyclopedia as your starting point—and then talk to us.
📩 Contact Soontrue with your products, target pack formats, and required capacity.

Our team will help you turn this knowledge into a tailored packaging machine or automated packaging line solution for your factory.