Understanding Packaging Machines: Working Principle and Core Components Explained
Packaging Knowledge Hub

If you're seeking packaging automation solutions, please contact us, and we'll be delighted to offer you the most tailored solution.
In modern industrial production, the efficiency and accuracy of your packaging processes significantly influence productivity and profitability. Given that the global packaging machinery market continues to grow rapidly—expected to exceed USD 60 billion by 2027 according to recent market trends—it becomes critical to understand how packaging machines work step by step, their core technologies, and selection strategies to enhance your packaging efficiency.
Let's dive into the detailed packing machine working principle and structural components of packaging machines, helping you make informed decisions.
How Packaging Machines Work Step by Step (Complete Workflow Explained)
Understanding the workflow of a Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) machine helps in troubleshooting and optimizing production. Here is the step-by-step process of how a roll of film becomes a finished package:
1. Material Conveying System: Key to Automated Feeding
The packaging process begins with precise and automated material handling. A reliable material conveying system integrates conveyors and sensors for accurate positioning.
Conveyor Types & Sensor Positioning: Conveyors can include belt, chain, and roller systems. Using sensors for precise positioning ensures materials align correctly, reducing errors and downtime. For instance, in food packaging, Soontrue designs contamination-proof conveyor systems to maintain hygiene standards (food-grade packaging machine requirements).
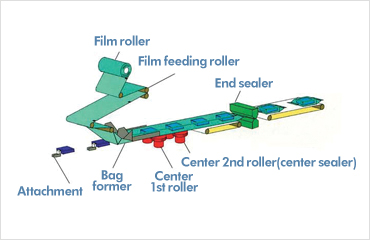
2. Packaging Forming: Flat Materials Transformed into 3D Packages
The forming stage converts flat materials into robust, secure packaging.
Hot vs Cold Forming (Packaging Forming Technology Choice):
Hot forming provides flexibility and strong seals ideal for food packaging, while cold pressing is energy-efficient and suited for certain pharmaceutical applications. Selecting the right forming method involves balancing energy usage and material compatibility (material compatibility in packaging forming).
3. Filling Process: Balancing Precision and Speed
Filling involves carefully balancing speed and accuracy to optimize efficiency without compromising quality.
Volumetric vs Weighing Fillers:
Volumetric fillers are suitable for liquids, ensuring consistency in beverages and sauces (automated liquid filling machine types). Weighing fillers handle granules or powders requiring precise dosage (pharmaceutical packaging machine sterilization).
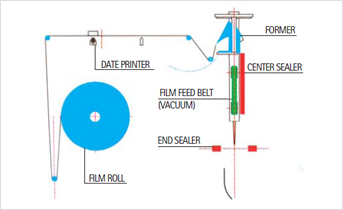
4. Sealing Technology: Ensuring Product Integrity and Aesthetics
Effective sealing is essential for product protection and consumer appeal.
Heat Sealing Temperature Parameters & Ultrasonic Sealing:
Accurately controlling temperature settings ensures strong, aesthetic seals. Ultrasonic sealing, often utilized in delicate products, reduces energy consumption and enhances seal quality (heat sealing temperature parameters).
Core Components of a Packaging Machine: A Deep Dive
1. Servo Motors: The Powerhouse for Precision
Servo motors drive critical packaging movements and positioning, offering precision and efficiency over stepper motors.
Servo Motor vs Stepper Motor in Packaging:
Servo motors provide higher accuracy, smoother motion control, and improved energy efficiency (high-precision servo motors for packaging). Brands like Panasonic and Mitsubishi are commonly used due to their reliability and performance, significantly reducing downtime (reducing downtime in packaging production).
2. Control Systems: The Brain of Packaging Automation
Advanced control systems automate machine functions, improving reliability and efficiency.
PLC vs Industrial PC Controls:
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) are popular due to reliability and ease of maintenance, while industrial PCs offer greater flexibility and data processing capabilities (PLC control system for packaging machinery). IoT integration further enables remote troubleshooting and predictive maintenance (IoT integration in packaging machinery).
3. Servo System: The Engine of Precision Motion Control
While the PLC acts as the "brain," the Servo Motor acts as the "muscle" of modern packaging machinery. Unlike traditional frequency conversion motors (VFD) that rely on simple speed regulation and mechanical braking, servo systems utilize closed-loop feedback. This allows the machine to track the exact position of the film and sealing jaws in real-time.
For high-speed packaging, the difference is critical:
Accuracy vs. Slippage: Frequency motors often struggle with inertia, leading to bag length errors of ±3-5mm. A servo-driven system precisely controls the start-stop motion, ensuring film pulling accuracy within ±1mm.
Dynamic Response: Servo motors provide high torque even at low speeds and can accelerate or decelerate instantly. This synchronization prevents the "film drift" often seen in older mechanical machines.
Smart Adjustments: When changing bag lengths, a servo system adjusts digitally via the HMI screen, whereas a frequency-based system often requires manual mechanical adjustments to cams or gears.
4. Auxiliary Systems: Sensors and Drive Mechanisms
Additional components enhance precision and extend machine life.
Sensor Calibration and Transmission Systems:
Photoelectric sensors with error compensation mechanisms ensure accurate positioning and detection (sensor calibration in automated packaging). Timing belts and gear transmissions need regular inspection to prevent breakdowns.
Industry Applications and Packaging Equipment Selection Guide
Understanding specific industry requirements can streamline your equipment selection (custom packaging machine solutions):
- Food & Beverage: Hygiene, contamination prevention, and consistent quality.
- Pharmaceuticals: Sterilization, traceability, GMP compliance.
- Personal & Household Care: Packaging aesthetics, flexible formats, consumer appeal.
Selection Checklist: Evaluate capacity, accuracy, scalability, and compatibility with future expansions (cost-effective packaging solutions for SMEs).
Energy Efficiency in Modern Packaging Technology
As production costs rise and sustainability goals become stricter, energy efficiency has moved from a "nice-to-have" to a critical selection factor. Modern packaging machines have evolved significantly from the power-hungry pneumatic systems of the past.
Key technologies driving this efficiency include:
- Servo-Driven "Energy on Demand": Unlike traditional motors that run continuously, servo motors consume power only when motion is required. They also generate less heat, reducing the load on factory air conditioning systems.
- Smart Standby Modes: Advanced PLC logic detects gaps in production. If the upstream feed stops, the machine automatically lowers the sealing jaw temperature and pauses the film drive to prevent energy waste and film burn.
- PID Temperature Control: Replacing simple on/off thermostats with PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers ensures sealing bars maintain precise temperatures with minimal power fluctuation, reducing energy consumption by up to 30% compared to legacy systems.
Emerging Trends: The Future of Packaging Automation
- Vision Inspection Systems: Machine vision ensures consistent quality through real-time product inspection.
- Sustainable Packaging: Increasing demand for biodegradable materials compatible with advanced packaging equipment (energy-saving packaging machine technologies).
Conclusion: Optimizing Your Packaging Efficiency through Technical Understanding
Choosing and operating a packaging machine requires deep knowledge of technical principles and market trends. Regular maintenance and technical optimization will maximize your equipment’s efficiency and lifespan.
Want to optimize your packaging solutions with expert advice and tailored solutions? Contact our Soontrue packaging specialists today.
FAQs about Packaging Machine Maintenance & Selection
Q: What is the working principle of a VFFS packaging machine?
A: The VFFS process follows 5 key steps: 1) Film Unwinding via tension rollers, 2) Bag Forming using a forming shoulder, 3) Vertical Sealing to create a tube, 4) Filling product via dosing systems, and 5) Horizontal Sealing and Discharge of the finished bag.
Q: Why are servo motors better than frequency motors for packaging?
A: Servo motors utilize closed-loop feedback to ensure film pulling accuracy within ±1mm, whereas frequency motors often struggle with inertia and slippage. Servos also provide instant acceleration and allow for digital bag length adjustments without mechanical changes.
Q: How do modern packaging machines improve energy efficiency?
A: Modern machines use servo-driven "energy on demand" systems that only consume power during motion. They also feature smart standby modes that lower temperatures during idle times and PID controllers that reduce energy fluctuations by up to 30%.
Q: What are the core components of an automatic packaging machine?
A: The core components include the PLC (Control System), HMI (Touch Screen), Servo Motors (Motion Control), Forming Shoulder (Bag Shaping), and Sealing Jaws (Temperature Control). High-quality components ensure long-term stability and precision.
Q:What daily maintenance steps are required for packaging machines?
A: Daily steps include inspecting belts, cleaning sealing jaws, verifying sensor calibration, and checking lubrication points regularly (maintenance checklist for packaging machines).
Q: How to quickly troubleshoot common servo motor failures in packaging machines?
A: Check for overheating, unusual noises, or positioning errors. Regularly monitor servo motor performance data for early detection and troubleshooting (common servo motor failures in packaging machines).
Q:How can small businesses choose a cost-effective packaging machine?
A: Small businesses should prioritize modular designs, ease of maintenance, energy efficiency, and scalability. Brands like Soontrue offer tailored options to meet SME needs effectively (how to choose a packaging machine for small businesses).
